Total Hardness as Calcium
Drilling fluid total hardness test is one of 10 articles that handle Testing Procedures For water based mud to be a full guide for drilling engineers and mud engineers. Water “hardness” refers to water that contains dissolved Calcium and Magnesium salts, which in high concentrations will reduce the effectiveness of Bentonite and polymers ( check also How to Design Polymer Mud), resulting in higher consumptions. The hardness of mix water is reduced with Soda Ash treatments ( Check also Major Drilling Fluid additives) to precipitate out the Calcium and Magnesium ions as Calcium and Magnesium Carbonate.

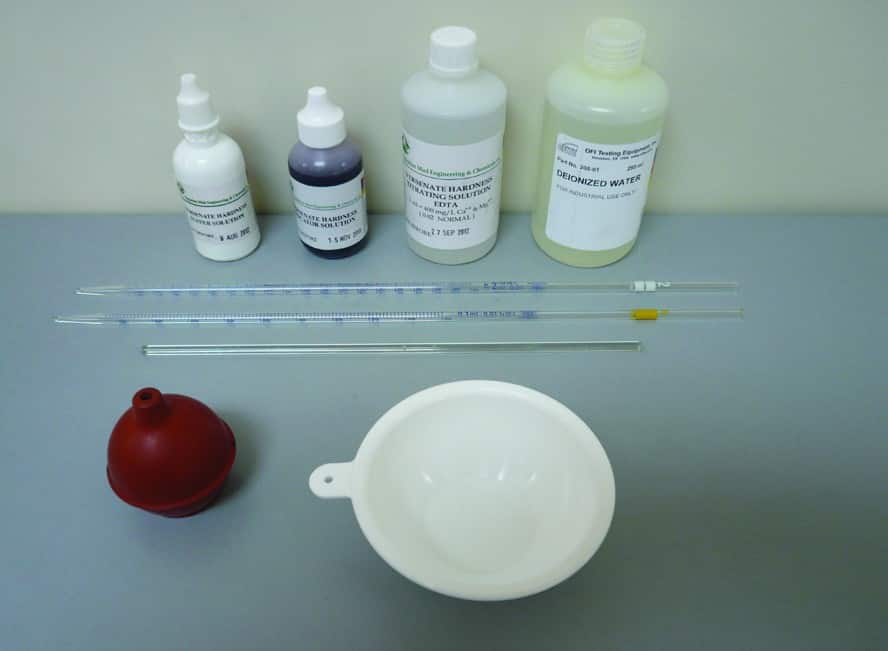
The following equipment is required for Drilling Fluid Total Hardness Test (Calcium and Magnesium) as Calcium:
- Distilled Water
- Ammonium Buffer Solution in dropper bottle
- Hardness Indicator Solution
- 0.02N EDTA Titrating Solution (0.01M)
- Graduated pipettes (1 ml and 2 ml)
- Titration dish (white ceramic or white polyethylene crucible)
- Glass Stirring Rod or Magnetic Stirrer with Bar Magnet
The procedure for measuring Total Hardness (Ca2+ and Mg2+) in mix water or mud filtrate is as follows:
- Add approximately 25 ml distilled water to a clean titration dish and place on a magnetic stirrer, if available.
- Use a magnetic stirrer with bar magnet to agitate the fluid in the titrating dish while adding the test chemicals, otherwise use a glass stirring rod.
- Add 10 drops of Ammonium Buffer solution.
- Add 5 drops of Drilling Fluid Hardness Test Indicator solution. If calcium and/or magnesium is present in the distilled water, a wine-red color will develop. If not, the solution will remain blue.
- Use a 1 ml pipette to transfer a 1 ml sample of mix water or mud filtrate into the titration dish, which will turn wine-red if calcium and/or magnesium are present.
- Titrate with 0.02N EDTA (0.01M) using a 2 ml graduated pipette while stirring the contents of the titration dish until the wine-red color turns blue (check carefully that all traces of red have been removed). See Figure 6 below.
When performing Drilling Fluid Hardness Test for mix water, a larger sample volume (e.g. 10 mls) should be used as this will give a more accurate result (the EDTA titration volume is then divided by the sample volume).
Calcium and Magnesium Ion Content Hardness Test In Drilling fluid
Drilling Fluid Hardness Test For Calcium Ion Content
The Calcium Ion Content of the filtrate sample is determined using a similar procedure for the total hardness, but using a different indicator solution.
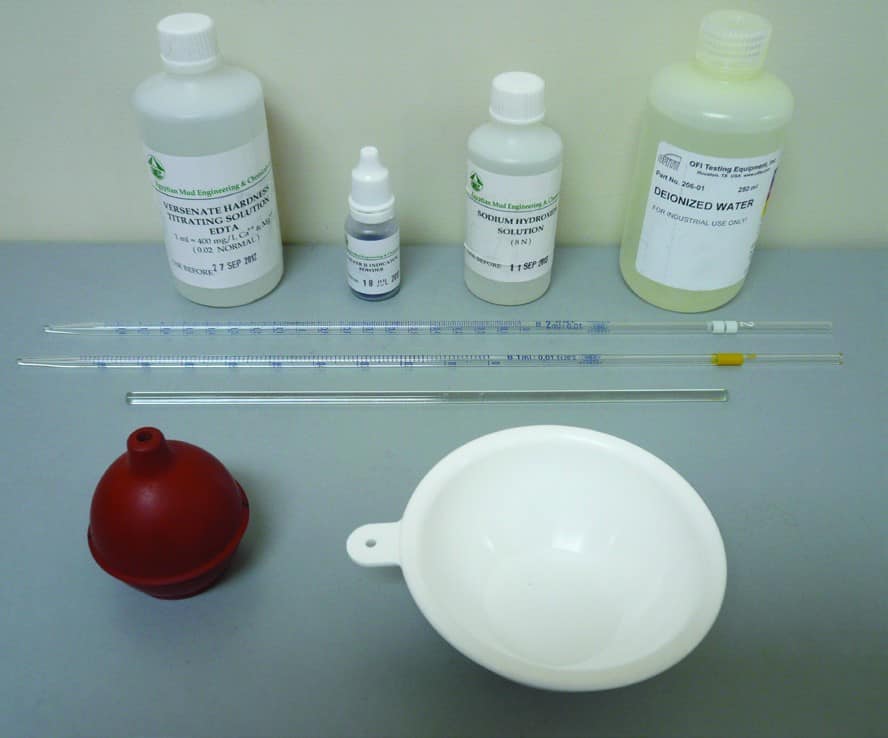

The following equipment is required for measuring Calcium Hardness:
- Distilled Water
- Calcium Buffer Solution (1N Sodium Hydroxide in a dropper bottle)
- Calver II Indicator in pillows or grains
- 0.02N EDTA Titrating Solution (0.01M)
- Graduated pipettes (1 ml and 2 ml)
- Titration dish (white ceramic or white polyethylene crucible)
- Glass Stirring Rod or Magnetic Stirrer with Bar Magnet
The procedure for measuring Calcium Ion Content in mud filtrate is as follows:
- Add approximately 25 ml distilled water to a clean titration dish and place on a magnetic stirrer, if available.
- Use a magnetic stirrer with bar magnet to agitate the fluid in the titrating dish while adding the test chemicals, otherwise use a glass stirring rod.
- Add 1 ml Calcium Hardness Buffer solution and several grains of Calver II indicator powder (a wine-red color will develop if calcium is present).
- Titrate with 0.02N EDTA (drop by drop) while stirring until the sample color changes from wine-red to blue, but do not go past the endpoint.
- Use a 1 ml pipette to transfer a 1 ml sample of mud filtrate into the titration dish.
- Add 2 drops of Calcium Buffer Solution (1N Sodium Hydroxide), which will precipitate out the magnesium ions as magnesium hydroxide.
- Add several grains of Calver II Indicator solution, turning the sample wine-red.
- Titrate with 0.02N EDTA (0.01M) using a 2 ml graduated pipette while stirring the contents of the titration dish until the wine-red color turns blue (check carefully that all traces of red have been removed). See below equation
Calcium Ion Content, mg/l = (ml of EDTA x 400) / (ml of sample used)
Drilling Fluid Hardness Test For Magnesium Ion Content
The Magnesium Ion Content can be calculated by subtracting the Calcium Ion Content from the Total Hardness. See the equation below.
Magnesium Ion Content, mg/l = [(Total Hardness, mg/l) – (Calcium, mg/l)]
If the water “hardness” is too high (i.e. high concentration of dissolved Calcium and Magnesium salts) then the effectiveness of Bentonite and polymers in the fluid system will be reduced, resulting in higher consumptions. Hardness can be reduced by treating the mix water or circulating system with Soda Ash or Sodium Bicarbonate, as this will precipitate out the Calcium and Magnesium ions as Calcium and Magnesium Carbonate.