The primary collapse loads are supplied by the pressure of the fluid column on the outside of the casing, which acts to collapse the pipe and may cause collapsed casing sticking problems. These fluids are usually the mud and possibly the cement slurry in which the casing pipe was set. Since the mud column increases with depth, collapse pressure is the highest at the bottom of the hole section and is zero at the surface. After finishing this article, you will be able to choose the right formula to calculate the collapse pressure.

The Importance of the Calculations & Formulas Of Collapse Pressure
Casing collapse pressure calculations are important because they help ensure the safety and integrity of oil and gas wells. The casing collapse can lead to several problems, including stuck pipes and loss of well control. By calculating the casing collapse pressure, drilling engineers can design wells that can withstand the external pressure exerted on the casing walls by drilling fluids and other materials. This calculation is also important in determining the maximum depth at which a particular casing can be safely installed, as well as in selecting the appropriate casing size and material for a given well design. Ultimately, casing collapse pressure calculations are crucial for ensuring that oil and gas wells can operate safely and effectively over the long term.
Collapse Pressure Formula
The formula to calculate the hydrostatic pressure acting at a particular depth is:
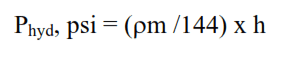
Where:
- ρm: is the density of the fluid in pcf.
- h: is depth in feet.
Casing Collapse Pressure Calculations Design
The worst-case of casing design conditions is when the casing is void of fluid, and the external force (collapse load) is the maximum mud weight when the Csg is run. In designing for collapse, the casing is assumed empty for the surface casing (one of the Types Of Casing), production casing, and partially empty for the intermediate casing.
Once the casing is cemented and the cement is set, the cement acts to help increase the collapse resistance.
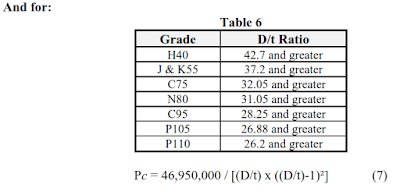
4 Formulas To Calculate Collapse Pressure
There are four formulas to calculate the casing collapse pressure (Pc) depending on the ratio of the pipe’s outer diameter to wall thickness.
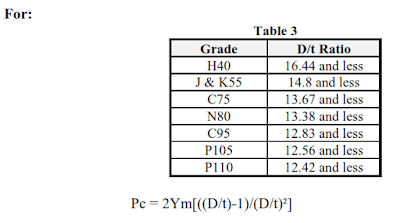
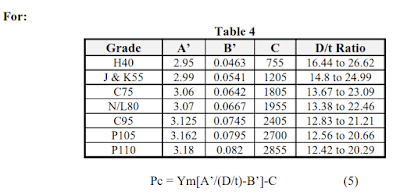
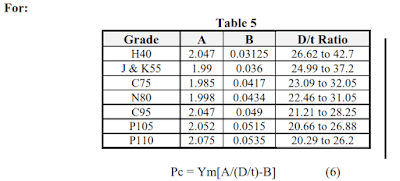
Example:
A string of 9-5/8″ 53.5# L-80 casing is to be set in 75 pcf mud at a depth of 6000 ft. Calculate the collapse rating for this casing and assume that the casing is empty. Then, determine if the Csg can safely be set to this depth to satisfy a safety factor for collapse of 1.125. Ym = 80,000 psi, ID = 8.535 in.
Solution:
Phyd = (75/144) x 6000 ft = 3,125 psi;
Since: De/t = 9.625 / 0.545 = 17.6605
We use Pc = Ym[A’/(D/t)-B’]-C
For N-80/L-80, A’ = 3.07; B’ = 0.0667; C = 1955
Pc = 80,000 [(3.07/17.6605) – 0.0667] – 1955 = 6616 psi
SF = 6616 / 3125 = 2.12
Allowable Collapse Pressure = 6616 psi / 1.125 = 5880 psi.
Therefore, from the previous casing collapse pressure calculations, the collapse load at 6000′ (3125 psi) is less than the allowable collapse (5880 psi), so it is safe to run.
I’m interested to know casing design as burst, collapse and tensile please send in details
Many thanks for helpful