
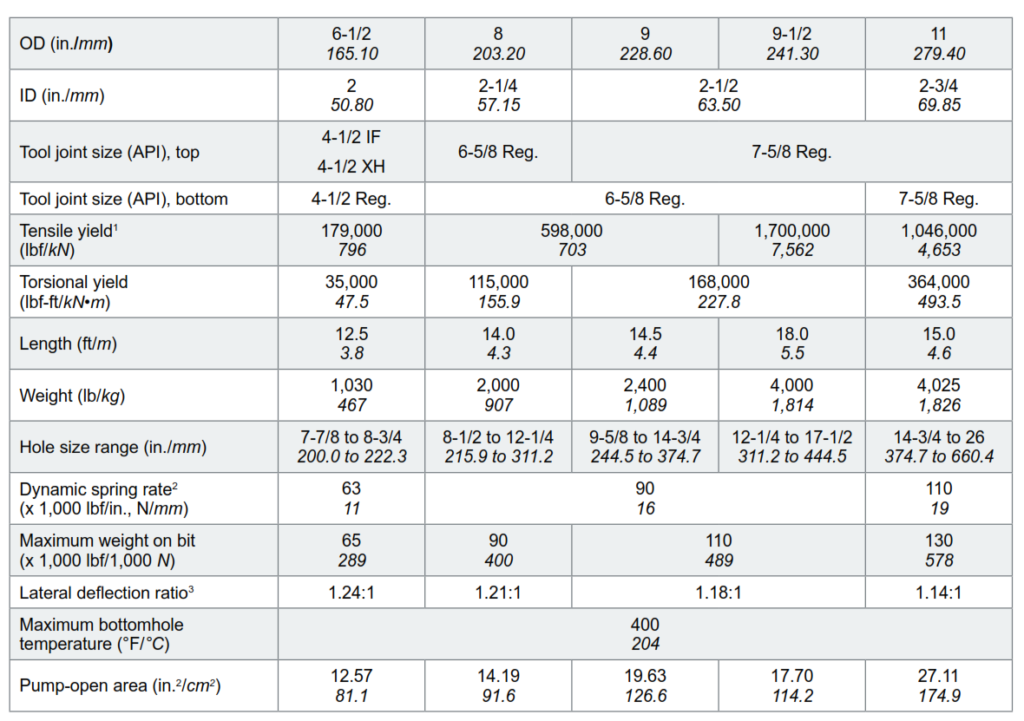
A shock absorber sub or damper is a mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses while drilling. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy (typically heat), which is then dissipated. Most shock absorber subs are a form of dashpot (a damper that resists motion via viscous friction).
So, You can consider the shock sub is the first line of defense against drill string vibrations that we encounter while drilling hard formations.
Purpose & Function Of Shock Sub
A Shock Absorber is used between the bit and drill collars to reduce the drill string’s vertical oscillation (bouncing). The primary benefit of shock absorption is that it allows for optimal weight and rotary speeds during drilling. This leads to increased penetration rates and lower drilling costs per foot. Various designs are available in the market, and your selection should be based on your specific situation. Some absorbers can function effectively even in high temperatures, while others do not require preloading. Additionally, those with special rubber can withstand drilling with more vibrations.
What Are The Drill Bit Oscillations?
Field studies have shown that the frequency of the oscillations was consistently three oscillations per revolution with a three-cone drill bit. It is believed that the bit does not drill the bottom of the hole evenly (completely flat), resulting in high and low places, with the number of high and low places being the same as the number of cutters on the bit. The peak-to-peak amplitude is approximately 0.5 inch. This bottom hole condition could account for the three oscillations per revolution when drilling with a three-cone bit.
How To Use Absorber To Eliminate The Drilling Bit Oscillations
The studies show that the placement of a shock absorber sub between the drilling bit and the drill collars can:
- Almost eliminate the vertical oscillations.
- Increases the bit footage (bit life): vertical bouncing causes fluctuations in the bit load, which hurts the bit footage
- It can reduce drill collar connection failures in hard formations by dampening the high fluctuating buckling.
- Reducing the amount of shocks can help boost your surface equipment’s performance and life.
It is highly recommended to perform maintenance on the sub after each trip to reduce the risk of tool failure. To do this, wash the mud from the polished mandrel and from inside the bottom connection. Check the polished mandrel thoroughly for any indications of corrosion, pitting, or flaking of the coating.
Limitations
Unfortunately, shock absorber subs are prone to mechanical failure due to the complexity of the device and the fact that they cannot be made as strong as the drill collars.
Positioning Of Shock Absorber Subs In The Drill String
For maximum effectiveness, the shock tool should be placed immediately above the bit to minimize the amount of unsprung mass below the tool. It is important that the tool is placed in a position where it is exposed to minimum side loading or bending stress.
Mechanism
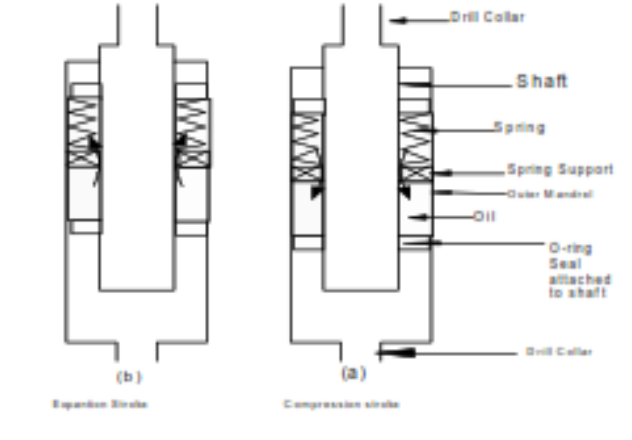
Ideally, the tool should have the same degree of stabilization at both ends to minimize buckling.
Vibrations from the bit cause the shaft to move inside the mandrel and compress the spring (compression stroke). Some of the drill string vibration force will not be transmitted to the drill string (check also: drill string design) above the tool because some of that force has been stored as energy in the spring, thus reducing the shock sub or impact on the drill string and drill pipe. As the shaft moves up (expansion stroke), the oil below the spring support between the shaft and mandrel is forced to flow through a slight restriction to the upper chamber. The oil flow generates a high-pressure drop, which is converted to heat, thus dissipating some of the lateral and axial vibration energy into heat.