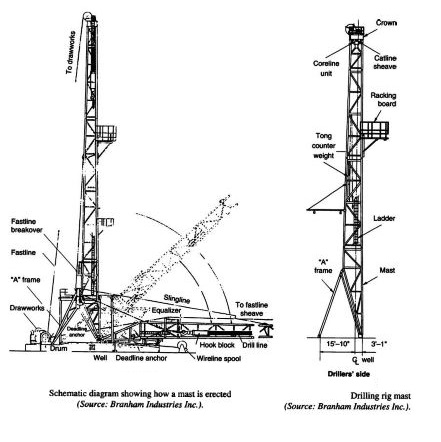
A Mast in drilling (Check also: Rig derrick) is a steel framework with a square or rectangular cross-section comprised of multiple sections assembled together and shaped like a very pointed A. It has the particular feature of being rotary jointed at the base so that it can be assembled or dismantled horizontally and then pulled to an upright position using the drawworks and a special hoisting cable.
Mast: A structural tower comprised of one or more sections assembled in a horizontal position near the ground and then raised to the operating position.
API Definition
Applications
The mast is normally used on land drilling rig types requiring a good deal of mobility; they are rarely used on offshore rigs. The racking board is in a cantilever position and lengths of drill pipe are racked on a floor, called the setback, that is separate from the mast structure. Most masts have one side open (window side), while others have both the front and rear side open (full view).
There are other less common types of masts that meet installation requirements on an offshore development platform (Platform Rig) where a conventional mast can not be placed in a horizontal position due to lack of room. The solution is to use a folding mast (Fig. 2) or a telescoping mast. The telescoping mast has two sections that fit together and are dismantled and laid down horizontally, taking up only half as much room.
Generally, masts are assembled on the ground in a horizontal position and are raised using drawworks. Some masts use telescopic sections and are assembled vertically (bootstrap). If the unit contains two or more sections, it may be telescoped or unfolded during the erection
procedure.
Mast Types
There are different types of masts for land drilling and service rigs:
- Folding Type
- Telescopic Masts
- Bootstrap Type
- Portable/Cantilivered masts (Non-Guy line)
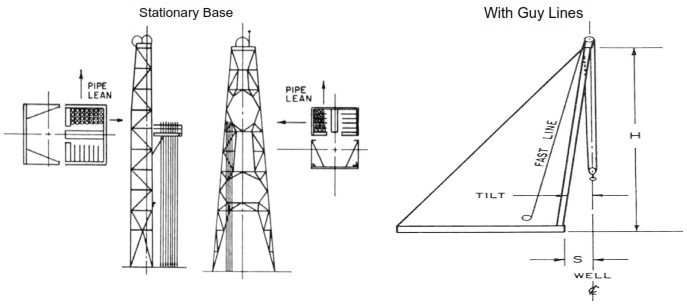

Portable Mast
Figure 4 shows a portable drilling mast in both vertical and horizontal positions.
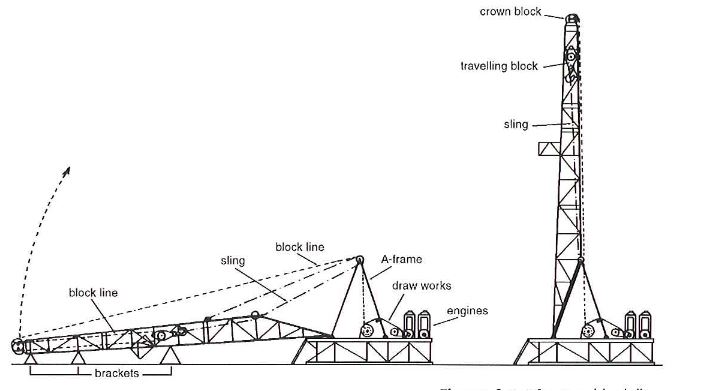
In principle, portable masts are always raised by their own traveling blocks and draw-works. The mast and engine substructure are installed first, then the engines and drawworks. The drawworks and engines are checked and prepared for running while the mast sections are being pinned together. The lower mast section is mounted by hinge pins to two brackets on the substructure.
An “A” frame is set up on the substructure and the block line is reeved so that the fast line runs over a sheave in this frame. The mast is raised by the block line and a raising sling which run over sheaves on the mast and the “A” frame. The procedure is illustrated in Figure 4. Once the mast is vertical it is locked in position to the “A” frame and is ready for use.
Raising The Mast
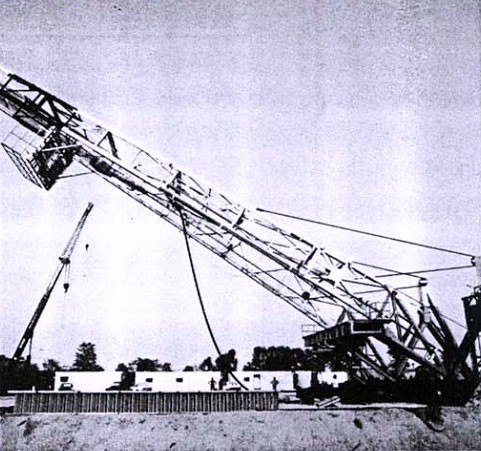
Considerable force is required to raise the mast from the horizontal position. The horizontal distance between the center of gravity and the hinge point, and thus the torque required, is the greatest (figure 5). This makes great demands on the lifting equipment and lifting must be carried out extremely slowly.
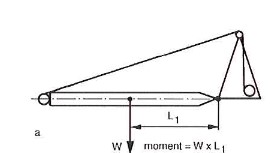
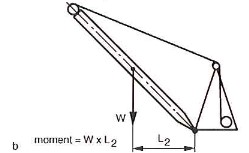
The further the mast is lifted the shorter the horizontal distance between the centre of gravity and the hinge point and the force required is correspondingly less (figure 6). Once the mast is vertical its weight is supported by the hinge point (Figure 7).
Distance L = 0.
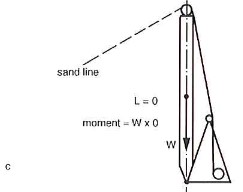
The mast will, however, fall slightly past the dead and point. Therefore only a small force will be needed to overcome the friction and lower the most post the dead point, a sand-line, for example, can provide this force. As soon as the mast has passed the vertical lowered by its own weight.
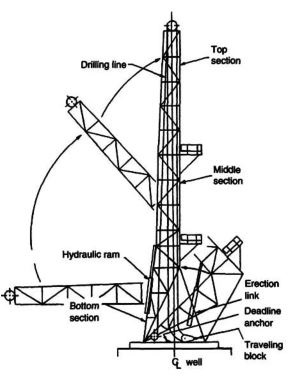
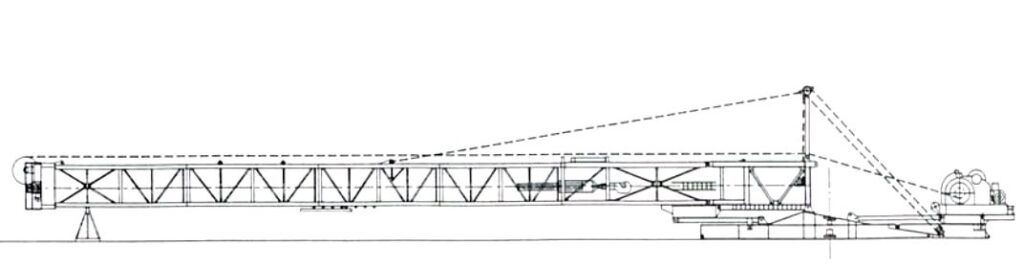
Telescopic Masts
Figure 8 shows a telescopic mast.
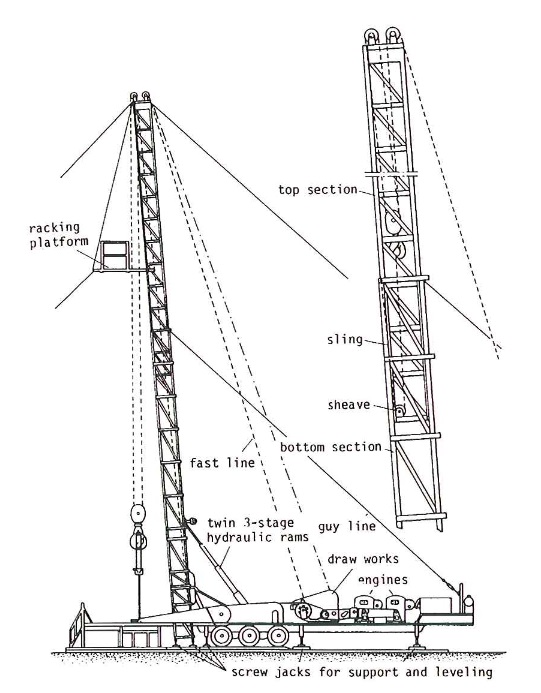
Telescopic masts with their drawworks and engines are usually mounted on trucks or trailers. The load should be borne by hydraulic or mechanical jacks, not by the tyres, so that the mast is kept steady and perpendicular. The jack feet are relatively small and, as large surface pressures are likely to occur, especially during fishing in drilling or while the casing is being run, wooden mats are usually laid to distribute the load before the truck or trailer is moved to the site.
Raising The Telescopic Mast
First, the bottom section, containing the upper section, is raised by two hydraulic cylinders to approximately 4 degrees past the dead center. This tilt makes it possible for the traveling block to be positioned slightly away from the mast, directly above the well once the erection of the mast has been completed.
After the lower section has been raised and guyed the rop section is extended by the raising sling and rig hoisting equipment (Rig Components). Some telescopic masts have a hydraulic cylinder to extend the top section.
Once in the highest position the rop section is locked to the lower section by the four pivot catches of the locking mechanism. The lower section must be locked securely by bolts or clamps so that no movement between the sections is possible. Since the lines to applied load are normally outside the base of a telescopic mast it must be used with guy lines to provide stability (see Figure 9).
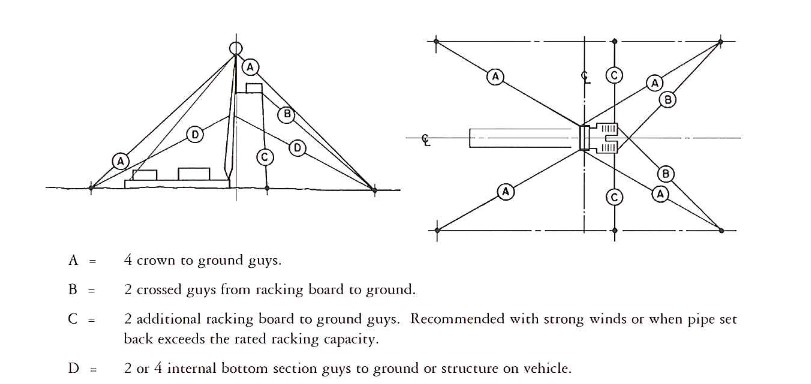
The thickness of the guy lines, the sequence and the tension at which these are fastened depend on the size and the construction of the mast. These values can be found in the instruction manual. Reference may also be made to API 4E for guy line specifications.
Standard Ratings & Specifications
Each structure shall be rated for the following applicable loading conditions. The following ratings do not include any allowance for impact. Acceleration, impact, setback, and wind loads will reduce the rated static hook load capacity.
Technical specifications are identical to those for derricks:
- Maximum hook load given the reeving system,
- Free height available in the mast,
- Width at the base,
- Resistance to wind with and without racked drill string.
- Capacities are comparable to those for derricks.
Standard Ratings For Mast With Guy Lines:
- Maximum-rated wind velocity (knots) without pipe setback.
- The maximum-rated wind velocity (knots) with full pipe setback.
- A maximum number of stands and size of pipe in the full setback.
- Maximum-rated static hook load capacity for a specified number of lines strung to the traveling block and the manufacturer’s specified guying.
Standard Ratings For Mast Without Guy Lines:
- Maximum-rated static hook load for a specified number of lines to the traveling block.
- The maximum-rated wind velocity (knots) without pipe setback.
- Maximum-rated wind velocity (knots) with full pipe setback.
- A maximum number of stands and size of pipe in the full setback.
- Rated static hook load for wind velocities varying from zero to maximum rated wind velocity with full rated setback and with a maximum number of lines to the traveling block.
Rigging Up
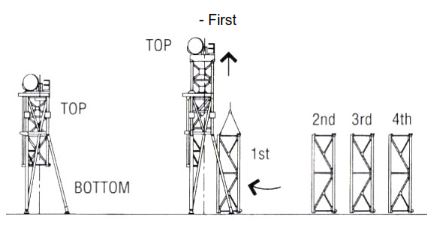
For conventional Mast (Land rig), the below pictures show the erection sequence of rigging up
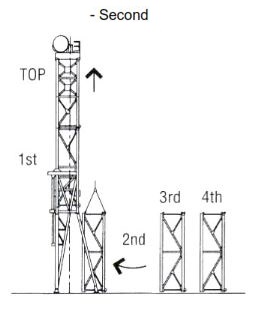
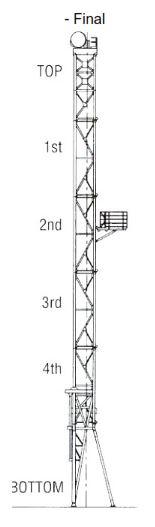
For rigging up the vertical mast, the below pictures show the bootstrap sequence of rigging up.
Mast Manufacturers
- National Oilwell Varco (Mfg.) TX – Houston
- Sovonex Technology Co., Ltd. (Dist.) Hong Kong – Kowloon – Kwuntong
- AFGlobal Corporation (Dist.) United States – TX – Houston
- Beijing KMC RIGS Co., Ltd (Mfg.) China – Beijing – Chaoyang
- Lee C. Moore (Mfg.) United States – OK – Tulsa
- Sinocoredrill Group Co., Ltd. (Mfg.) China – Chongqing
- Sunnda Corporation (Mfg.) United States – TX – Houston
- Trevi Finanziaria Industriale S.p.A. (Mfg., Svc.) Italy – Forli-Cesena – Cesena
- Xuzhou Hengxing Jinqiao Machinery Technology Co., Ltd. (Mfg.) China – Jiangsu – Xuzhou
- Derrick Services Limited (Mfg., Svc.) United Kingdom – Norfolk – Great Yarmouth
- MAIT USA Corp. (Mfg.) United States – TX – Humble
- Veristic Technologies, Inc. (Mfg.) United States – TX – Houston
- Superior Derrick Services, LLC (Mfg., Svc.) United States – LA – Martinville