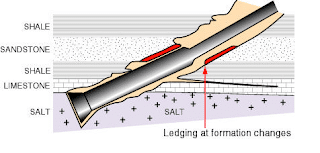
Ledge in Drilling: The wellbore passes through the rock of varying types and ledges develop at the interfaces between layers of differing hardness.
Closely spaced ledges decrease the effective diameter of the hole and produce a “shouldered” hole surface. Any type of casing string requires a smooth, more in-gauge hole diameter for free passage and not to have a pipe sticking problem.
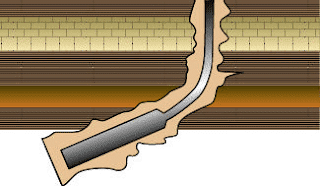
Doglegs: While drilling a wellbore, the characteristics of the rock cause the drilling bit to be deflected and can result in a change in Azimuth.
Likewise, when drilling with a directional Drilling Bottom Hole Assembly, sudden changes in angle can cause a kink in the wellbore direction. Sharp deviations in wellbore direction are called doglegs.
Ledges & Doglegs Environment:
There are some situations that increase the possibility of this problem:
- When an unsuitable Bottom Hole Assembly BHA is run.
- After a change in Bottom Hole Assembly BHA.
- Prognosed hard soft interbedded formations.
- Prognosed fractured / faulted formations.
- After direction changes.
- While POOH.
Preventative Action To Avoid Ledges and Doglegs In Drilling
- Ledging can be reduced by using a packed hole assembly.
- Minimize direction changes in the well bore.
- Try to keep Bottom Hole Assembly BHA configuration constant.
- Reaming also is important.
- Record depths of ledges.
- you can bring a large scale printout from the mud loggers (Mud logger Job Description) and to draw a scale Bottom Hole Assembly BHA on a separate piece of paper. The paper Bottom Hole Assembly BHA can be positioned at the depth of any Overpulls and it is easy to see if any of the drilling stabilizers are hanging up at the same point. By using this technique it is simple to keep track of multiple problem zones and to communicate expected problem depths clearly to the driller (Check also Driller Job Descriptions).
- Survey with sufficient frequency. Increasing the wellbore survey frequency will:
- assist in evaluating/reducing well bore tortuosity.
- reduce the number of Bottom Hole Assembly BHA changes.
- Slow tripping pipe speeds before Bottom Hole Assembly BHA enters the suspected ledges zone or dog legs. Avoid prolonged circulation across soft inter bedded formations.

- Limit initial set down weight to less than 50% of down Drag to minimize momentum effects when running into a tight zone. Do not start angle building operations too close to the shoe (start at least 30m below old hole)
Ledges and Doglegs Stuck Indications Tips
- If you encountered Sudden erratic overpull or setdown.
- Problems are at fixed depths.
- Full circulation is possible.
How To Free ledges and doglegs stuck In Drilling?
- If moving up when ledges and doglegs sticking occurred, apply torque and jar down with maximum trip load.
- If moving down, using drilling jar to jar up with maximum trip load. Do not apply torque.
- If able to, backream or ream very slowly past problem as rotation will assist the Stabilizers and/or other Bottom Hole Assembly BHA Components to roll past the ledge.