Coiled Tubing (CT) is a continuous length of small-diameter pipe that is spooled onto a reel in the same way as wire or cable is wrapped on a drum. The coiled tubing operation permits the technique of “snubbing” a continuous length of tubing in and out of a live well through a stripper BOP arrangement. The main advantage of Coiled Tubing is that it can be run into producing wells, against high wellhead pressures (e.g. 345 bar / 34,500 kPa or 5000 psi), and down past the perforations, without production interruption or killing the well (Wait and Weight – Driller’s Method). The most common pipe size in use is 1.5″ through to 2.875″, although larger sizes are available and used.
Check also Coiled Tubing Handbook PDF download
In an offshore environment, Coiled Tubing can be run into a well as quickly as 3 hours, after positioning the equipment on deck. When truck mounted for land operations, this time can be cut to 1.5 hours after rig up on site. With the addition of a maximum working depth of 7700m (25,000 ft), which can be achieved at running speeds of 79m/minute (260 ft/minute), it can be seen that Coiled Tubing is a very cost-effective way of performing downhole work.
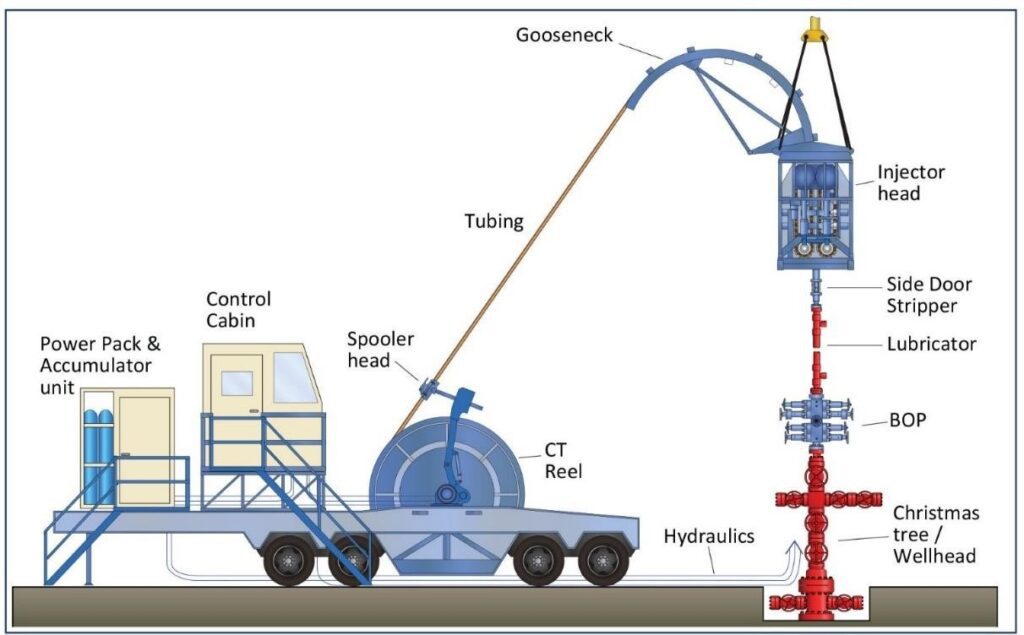
The standard coiled tubing package can be defined in terms of the surface equipment needed to safely trip the coiled tubing in and out of the well:
- Coiled Tubing
- Reel Unit
- Power Pack
- Control Unit
- Tubing Injector Unit
- CT Pressure control equipment – Blowout Preventers (including lubricator and side door stripper)
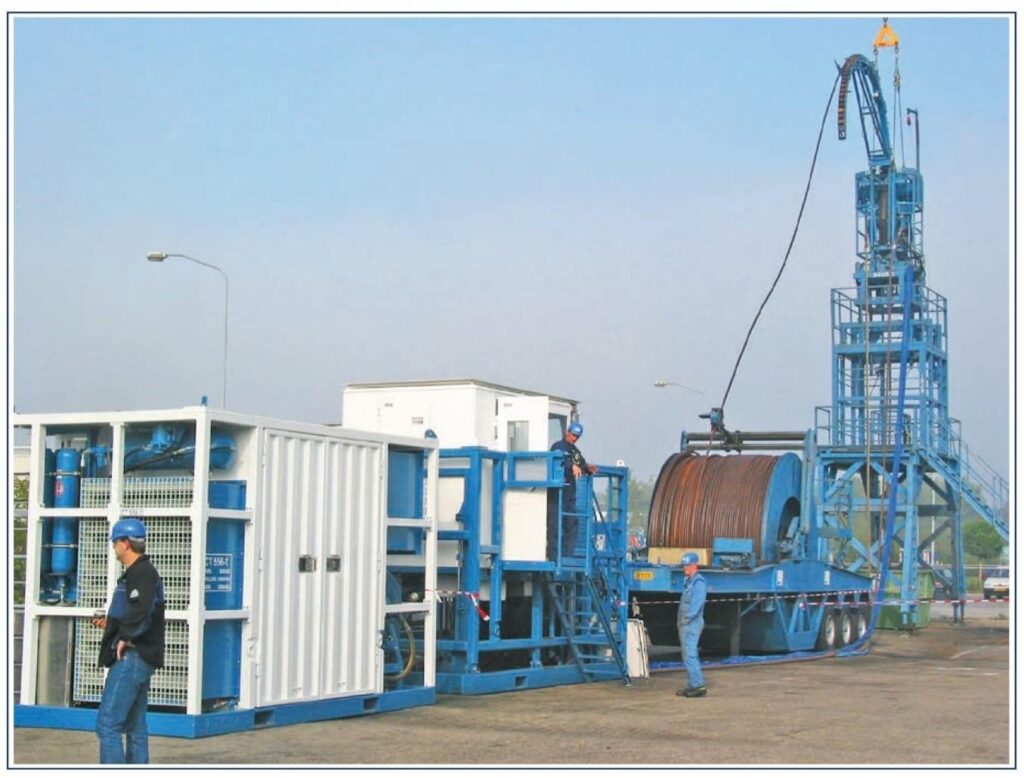
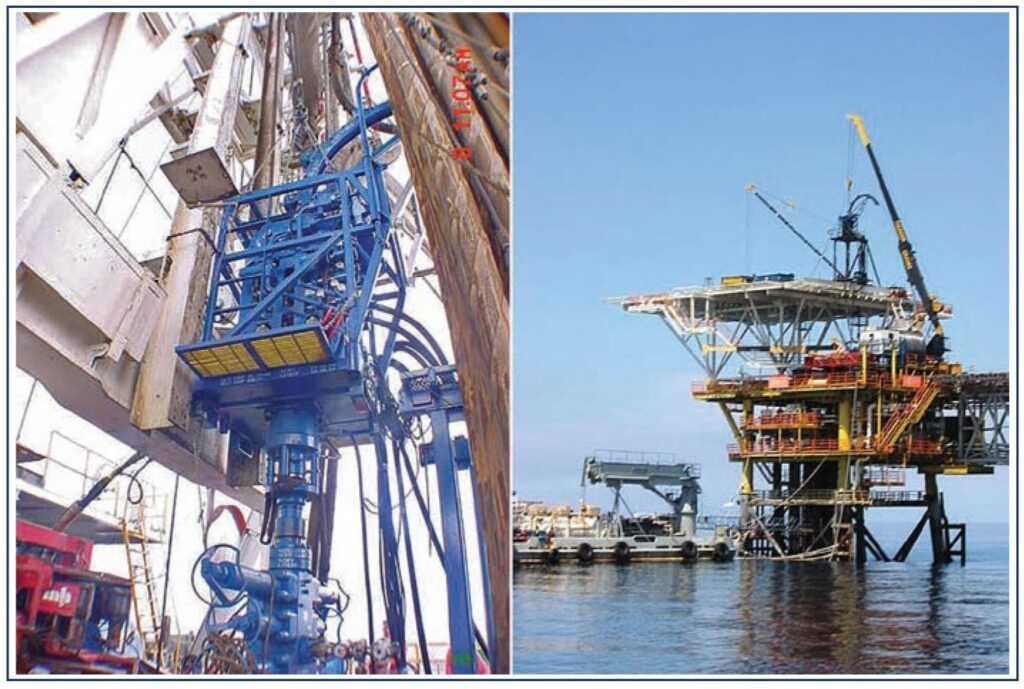


Auxiliary Coiled Tubing equipment is needed to ensure that the tubing is run to the required depth and that the operating envelope (pressure, weight, etc.) of the equipment is not exceeded throughout the duration of the task. Additional equipment associated with the task type is also required, such as nitrogen tanks for nitrogen displacement, or downhole tools, such as a mill and motor for milling in drilling operations, a downhole mud motor for coiled tubing drilling.
This Topic provides an overview of the available surface equipment, however as technology develops, the range of tools may be enhanced for most applications.
A range of coiled tubing packages/units is available from the service companies. The selection of this equipment is predominantly determined by the intended application and well completion conditions, i.e. sour service, CT size, etc. Additionally, hybrid units are available which enable the retrieval of conventional tubular, or other well preparation tasks requiring conventional operations, prior to commencing the coiled tubing work. These hybrids have been developed predominantly in response to well re-entry requirements and coiled tubing drilling.
The full suite of surface equipment used during coiled tubing operations will vary depending on the job to be performed.
However, the following principal items of equipment are considered to be standard:
- Primary Equipment
- CT Reel Unit
- Injector Head (including “gooseneck”)
- Power Pack
- Control Cabin (e.g. load / depth indicators)
- Pressure / Well Control Equipment (check also: Well Control)
- Stuffing Box
- Quad Blowout Preventers (BOP)
- Shear Seal BOP
- Annular BOP (optional)
Applications
Coiled tubing is used in long, horizontal wells, or instead of cable if drilling or completion fluid is to be circulated in the well. Coiled tubing can be used for both well workover and well drilling.
Its advantage compared to cable operations (Wireline) is that it is possible to circulate fluid into the well. The coiled tubing also has greater strength than cable and can carry the weight of longer and heavier tool string. It can also be used in wells that have a long, horizontal, and complicated well trajectory (check well trajectory calculations).
Its applications on Workover Wells:
- Acid stimulation of limestone formations,
- Maintenance and washing of the wellbore
- Perforation
- Start-up of the well with light liquid
- Installation of completion equipment
- Gravel packing
- Fishing in drilling operations.
Several drilling operations have also been carried out with CT as a work string, but drilling operations with it are not common in some places.
The Coiled Tubing
Coiled tubing describes a long tube that is rolled into a reel. The pipe is made of a steel alloy which makes the material flexible and at the same time strong.
The tube is made of plates that are rolled into a cylindrical shape. The open cylinder proceeds to a welding arrangement that welds the ends of the plate together along the length of the pipe. It is all produced as one long tube which is fed onto a storage drum.
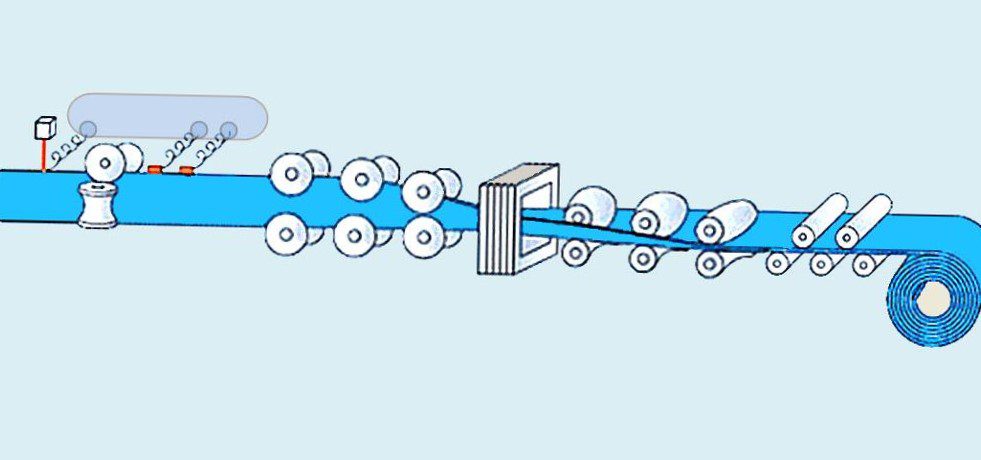
It can be bent around the drum core without breaking or collapsing, but the pipe is permanently deformed by the curve to which it is bent. When the tube is pulled off the drum, it is slightly curved due to the bending it is subjected to on the drum.
Running In Hole
The tube is pulled off the drum by CT injector mounted on top of the well. The injector pulls the tube off the drum, while a small motor mounted on the core of the drum holds the counter (brake) so that the drum does not spin the entire length of the tube out freely ( runaway tubing ).
When the pipe passes through the injector, it is straightened slightly before entering the well. When the CT is pulled out of the well, the operator changes the direction of travel on the injector, so that it pulls the pipe out of the well. At the same time, the drum rolls by means of the motor, so that the pipe is rolled nicely on the drum.
The Barriers
When CT is to be run into the well, a coiled tubing BOP and two strippers are connected at the top of the well. They act as external barriers. In addition, two one-way valves are mounted in the bottom of the coiled tubing, so that there is no outflow from the well through it to the surface.
Coiled tubing compared to wireline and drilling
| Coiled tubing | Drill Pipe | Cable |
|---|---|---|
| avoids stopping while pipe tripping RIH & POOH to connect pipes together or apart ( connection ) | must stop and make connections for each stand | faster RIH/POOH than both coiled tubing and drill pipe |
| allows fluids circulation | allow fluids circulation | circulation is not possible |
| long-range and thrust | long-range and thrust | long-range but small thrust |
| good traction | best traction | small traction |
| can be used for drilling | is best suited for drilling | can not drill |
| can not rotate the tube but Bottom Hole Assembly | can rotate both tubes and any types of the Bottom Hole Assembly | can not rotate cable or tools |
| flexible, can go in spiral lock in the well | stiff and stable | without structural rigidity, must be kept in tension to avoid cable knot |
| withstands some hole friction | very good against hole friction | does not tolerate hole friction |
| The pipe is weakened by bending loads from the drum, the gooseneck and the injector. It must be cut after some time. | The pipes have a very long duration. They can be cut, a new thread box can be fitted, and they can be reused. | The cable has a good safety margin for the load. It is cut/replaced when it achieves a life limitation. |
Coiled Tubing Capacities
| Size OD in | Wt/Ft Ib | ID in | Bbl / Lin Ft | Lin Ft/Bbl | Cu Ft/Lin Ft | Lin Ft/ Cu Ft | Gal/ Lin Ft | Lin Ft/ Gal |
| 1 | .743 | .850 | .00070 | 1424.8 | .00394 | 253.77 | .0295 | 33.924 |
| .850 | .826 | .00066 | 1508.8 | .00372 | 268.73 | .0278 | 35.924 | |
| .920 | .810 | .00064 | 1569.0 | .00358 | 279.45 | .0268 | 37.357 | |
| .981 | .796 | .00062 | 1624.6 | .00346 | 289.37 | .0259 | 38.683 | |
| 1.040 | .782 | .00059 | 1683.3 | .00334 | 299.82 | .0250 | 40.080 | |
| 1 1/4 | .944 | 1.100 | .00118 | 850.7 | .00660 | 151.53 | .0494 | 20.256 |
| 1.083 | 1.076 | .00112 | 889.1 | .00631 | 158.36 | .0472 | 21.170 | |
| 1.175 | 1.060 | .00109 | 916.2 | .00613 | 163.18 | .0458 | 21.814 | |
| 1.254 | 1.046 | .00106 | 940.9 | .00597 | 167.58 | .0446 | 22.402 | |
| 1.332 | 1.032 | .00103 | 966.6 | .00581 | 172.16 | .0435 | 23.014 | |
| 1.506 | 1.000 | .00097 | 1029.4 | .00545 | 183.35 | .0408 | 24.510 | |
| 1.601 | .982 | .00094 | 1067.5 | .00526 | 190.13 | .0393 | 25.417 | |
| 1.827 | .938 | .00085 | 1170.0 | .00480 | 208.39 | .0359 | 27.857 | |
| 2.014 | .900 | .00079 | 1270.9 | .00442 | 226.36 | .0330 | 30.259 | |
| 1 1/2 | 1.429 | 1.310 | .00167 | 599.8 | .00936 | 106.84 | .0700 | 14.282 |
| 1.527 | 1.296 | .00163 | 612.9 | .00916 | 109.16 | .0685 | 14.593 | |
| 1.623 | 1.282 | .00160 | 626.3 | .00896 | 111.56 | .0671 | 14.913 | |
| 1.840 | 1.250 | .00152 | 658.8 | .00852 | 117.34 | .0638 | 15.686 | |
| 1.960 | 1.232 | .00147 | 678.2 | .00828 | 120.80 | .0619 | 16.148 | |
| 2.245 | 1.188 | .00137 | 729.4 | .00770 | 129.91 | .0576 | 17.366 | |
| 2.483 | 1.150 | .00128 | 778.4 | .00721 | 138.64 | .0540 | 18.533 | |
| 1 3/4 | 1.915 | 1.532 | .00228 | 438.6 | .01280 | 78.12 | .0958 | 10.443 |
| 2.175 | 1.500 | .00219 | 457.5 | .01227 | 81.49 | .0918 | 10.893 | |
| 2.318 | 1.482 | .00213 | 468.7 | .01198 | 83.48 | .0896 | 11.160 | |
| 2.662 | 1.438 | .00201 | 497.8 | .01128 | 88.67 | .0844 | 11.853 | |
| 2.951 | 1.400 | .00190 | 525.2 | .01069 | 93.55 | .0800 | 12.505 | |
| 2 | 2.207 | 1.783 | .00309 | 323.8 | .01734 | 57.67 | .1297 | 7.710 |
| 2.509 | 1.750 | .00297 | 336.1 | .01670 | 59.87 | .1250 | 8.003 | |
| 2.677 | 1.732 | .00291 | 343.2 | .01636 | 61.12 | .1224 | 8.170 | |
| 3.080 | 1.688 | .00277 | 361.3 | .01554 | 64.35 | .1163 | 8.602 | |
| 3.419 | 1.650 | .00264 | 378.1 | .01485 | 67.35 | .1111 | 9.003 | |
| 2 3/8 | 3.011 | 2.125 | .00439 | 228.0 | .02463 | 40.60 | .1842 | 5.428 |
| 3.215 | 2.107 | .00431 | 231.9 | .02421 | 41.30 | .1811 | 5.521 | |
| 3.706 | 2.063 | .00413 | 241.9 | .02321 | 43.08 | .1736 | 5.759 | |
| 4.122 | 2.025 | .00398 | 251.0 | .02236 | 44.71 | .1673 | 5.977 | |
| 4.445 | 1.995 | .00387 | 258.6 | .02171 | 46.07 | .1624 | 6.158 | |
| 2 7/8 | 3.932 | 2.607 | .00660 | 151.5 | .03707 | 26.98 | .2773 | 3.606 |
| 4.554 | 2.563 | .00638 | 156.7 | .03583 | 27.91 | .2680 | 3.731 | |
| 5.059 | 2.525 | .00619 | 161.5 | .03477 | 28.76 | .2601 | 3.844 | |
| 5.462 | 2.495 | .00605 | 165.4 | .03395 | 29.45 | .2540 | 3.937 | |
| 3 1/2 | 6.230 | 3.150 | .00964 | 103.7 | .05412 | 18.48 | .4048 | 2.470 |
| 6.733 | 3.120 | .00946 | 105.7 | .05309 | 18.84 | .3972 | 2.518 |